Sinusitis
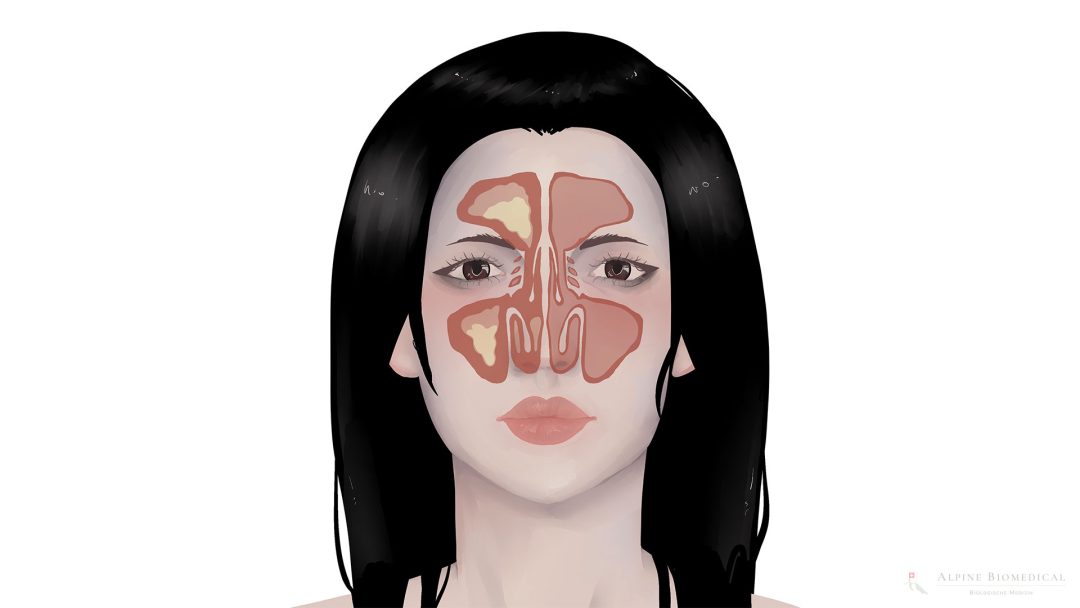
Sinusitis is a common disease in which the mucous membranes in the paranasal sinuses become inflamed. Typical symptoms include headaches, nasal congestion, nasal discharge, a reduced sense of smell and a feeling of pressure in the ears. Paranasal sinuses have a close relationship with the maxillary posterior teeth. Therefore, especially in the case of unilateral sinusitis, a dental examination should also be considered.
What is Sinusitis?
The paranasal sinuses are air-filled cavities that are in direct contact with the nose. They have the task of warming and humidifying the inhaled air. It is also thought that they serve as a resonance chamber for the voice and to reduce the weight of the head. The paranasal sinuses expand in the course of life and take up more and more space. The connections between the paranasal sinuses and the nasal cavity are fine and can become blocked, e.g. during a cold. As a result, sinusitis develops quite frequently. The mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses thickens and closes the entire cavity. Those affected complain of the typical symptoms.
Sinusitis is differentiated according to its localization:
- Maxillary sinusitis (maxillary sinusitis)
- Frontal sinusitis (sinusitis frontalis)
- Ethmoid sinusitis (sinusitis ethmoidalis)
- Sphenoid sinusitis (sinusitis sphenoidalis)
- Pansinusitis
Maxillary Sinusitis
The maxillary sinuses are located in pairs under the eyes and above the maxillary posterior teeth. The maxillary sinuses are often affected by inflammation. Those affected experience a feeling of pressure or pain under the eyes. Depending on the cause and spread, pain may also be felt in the teeth.
Due to the close connection between the maxillary sinuses and the teeth, an inflammation of the maxilla can cause maxillary sinusitis. Due to the proximity to the eyes, it is rarely possible for the infection to spread to the eyes, which poses a risk in the case of maxillary sinusitis.
Ethmoid Bone Cell Inflammation
The ethmoid cells are located between the eyes. They consist of small cavities and ducts. They also frequently become inflamed and can cause discomfort. Patients complain of increased pressure or pain between the eyes. Due to their proximity to the eyes and the brain, the inflammation can be dangerously transmitted.
Frontal Sinusitis
Frontal sinusitis is also common. The frontal sinuses are located in pairs in the frontal bone and can cause a feeling of pressure or pain in the forehead in the event of inflammation. The frontal lobe of the brain is located behind the frontal sinuses. As a complication, this infection can also go into the brain, which should be prevented at all costs.
Sphenoid Sinusitis
The sphenoid sinus is located behind the ethmoid cells and is located in the center of the head. This is what makes sphenoid sinusitis so dangerous. Although it is rare for the inflammation to spread to the brain, it can lead to serious complications. In the case of sphenoid sinusitis, those affected complain of headaches, whereby the pain can radiate to the ears.
Pansinusitis
In pansinusitis, all the maxillary sinuses are inflamed at the same time. The most common causes of pansinusitis include a viral infection during a cold or an allergy-induced thickening of the mucous membranes of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
Paranasal Sinusitis Symptoms
In terms of symptoms, a distinction can be made between acute sinusitis and chronic (permanent) sinusitis.
In the acute form, the symptoms are much more intense and noticeable:
- Throbbing and radiating pain in the area of the eyes, cheekbones, upper jaw teeth and forehead
- Headache
- Increased pain when bending the head forward and when stepping with the foot
- Discharge from the nose
- Stuffy nose
- Feeling of pressure in the ears
- Impaired sense of smell
- Possibly fever and symptoms of illness
Chronic sinusitis can go unnoticed for years and progresses with few or no clear symptoms. This is what makes chronic sinusitis so dangerous, because as a silent inflammation, it can develop a permanent physical burden.
Causes of Sinusitis
The following factors are discussed as causes of sinusitis:
- Viral infections (adenoviruses or rhinoviruses)
- Bacterial infections
- Infection with fungi
- Allergic reactions, for example hay fever
- Jaw inflammation in the upper jaw
- Anatomical constrictions, e.g. curvature of the nasal septum
- Nasal polyps that block ventilation
- Weakened immune system
- ASS intolerance (allergy to acetylsalicylic acid)
- Histamine intolerance
- Food intolerances
- Smoking
- Intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal problems
Is Sinusitis Contagious?
Sinusitis can be contagious, depending on the cause. For example, sinusitis with a viral cause is contagious. The viruses can be transmitted as a droplet infection through sneezing or coughing and infect other people.
The risk of infection is highest when the symptoms of the illness are at their peak.
People with a healthy immune system are much better protected from infection with the transmitted rhinoviruses or adenoviruses.
Treating Sinusitis
When it comes to treatment, a distinction should be made between symptomatic and causal measures. Symptomatic measures include decongestant nasal sprays, the use of mucolytics and painkillers. In the case of a severe bacterial infection, antibiotic treatment may also be necessary.
Inhalations, nasal rinsing, warm drinks and rest also help to alleviate the symptoms.
A thorough clarification of the causes should take place before a cause-oriented treatment. This includes clarification of anatomical constrictions, immune disorders, intolerances and intestinal problems.
A balanced and resilient immune system is crucial for defending against diseases and maintaining health. Particular attention should be paid to a thorough intestinal flora diagnosis, as over 80% of the immune system is located in the intestine. Proper intestinal cleansing is recommended to achieve optimal intestinal health. Furthermore, measures such as hyperthermia, ozone therapy of the blood, but also infusion therapies can be effective in the treatment of sinusitis.
Med. pract. Dana Hreus M.A.
Chronic sinusitis can act as silent inflammation and place a permanent burden on the body. A thorough diagnosis lays the foundation for effective, cause-oriented therapy.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.