Atopic Dermatitis
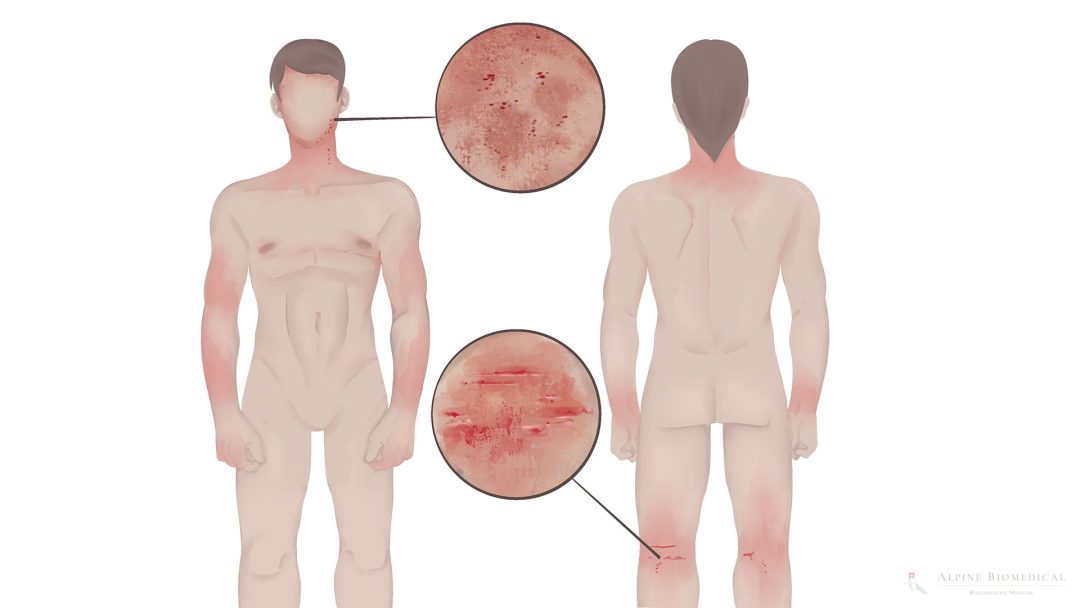
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic recurring skin disease, also known as atopic eczema or neurodermitis. The term neurodermatitis is misleading and comes from the earlier misconception that the cause of the disease was nerve inflammation.
Atopic dermatitis occurs in childhood, improves over the years or heals by around the age of 20. The disease progresses in episodes and manifests itself as a reddened, cracked, scaly and itchy area of skin.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis has the following symptoms:
- Reddened and sensitive skin
- Dry, cracked and scaly skin
- Itching and a desire to scratch the skin areas
- Weeping skin areas with the formation of crusts
Scratching should be avoided at all costs in order to prevent infection and scarring.
Cause of Neurodermatitis
The cause of neurodermatitis has not yet been conclusively clarified. This disease is most likely caused by various factors:
- A dysregulation of the immune system with a so-called TH2 shift. This leads to hyperfunction of type 2 T helper cells, which are particularly specialized in extracellular allergens
- Disorders in the autonomic nervous system
- An enzyme defect in fat metabolism
- Environmental factors or environmental toxins
- Disturbed intestinal flora and permeable intestinal mucosa (leaky gut)
- Food intolerances
- Increased stress
- Synthetic clothing and wool
Diagnosis and Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
The diagnosis is made by the dermatologist based on the typical symptoms and the affected areas of the body. Further diagnosis to determine the cause more precisely is important and can help to have a profound effect on the disease.
Treatment involves restoring the skin’s protective barrier, avoiding trigger factors and using anti-inflammatory creams. Restoring the skin’s protective barrier is particularly important as it prevents secondary complications such as inflammation and fungal infections.
In terms of a holistic approach, the avoidance of damaging factors should also be observed – this means avoiding smoking, synthetic fabrics in clothing as well as wool, caution when coming into contact with irritating chemical substances (e.g. cleaning agents) and avoiding scratching the affected areas of skin. Diet is also an important factor. People with atopic dermatitis should avoid caffeine and prefer an anti-inflammatory and alkaline diet. Intestinal health should also not be neglected and a targeted, individually tailored intestinal cleanse should be carried out.
Med. pract. Dana Hreus M.A.
Neurodermatitis can severely impair quality of life. Those affected can be helped with a holistic diagnosis and therapy.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.