Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, also known as Lupus erythematosus, is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease belonging to the collagen vascular disease group. It arises from the formation of autoantibodies against nuclear components, leading to inflammatory damage to the body’s connective tissue. Environmental factors and genetic predisposition are discussed as potential causes of Lupus.
Symptoms of Lupus
There are two main forms: cutaneous lupus, exclusively affecting the skin, and systemic lupus, presenting a more severe clinical picture that can theoretically affect any organ.
Typical symptoms of Lupus include:
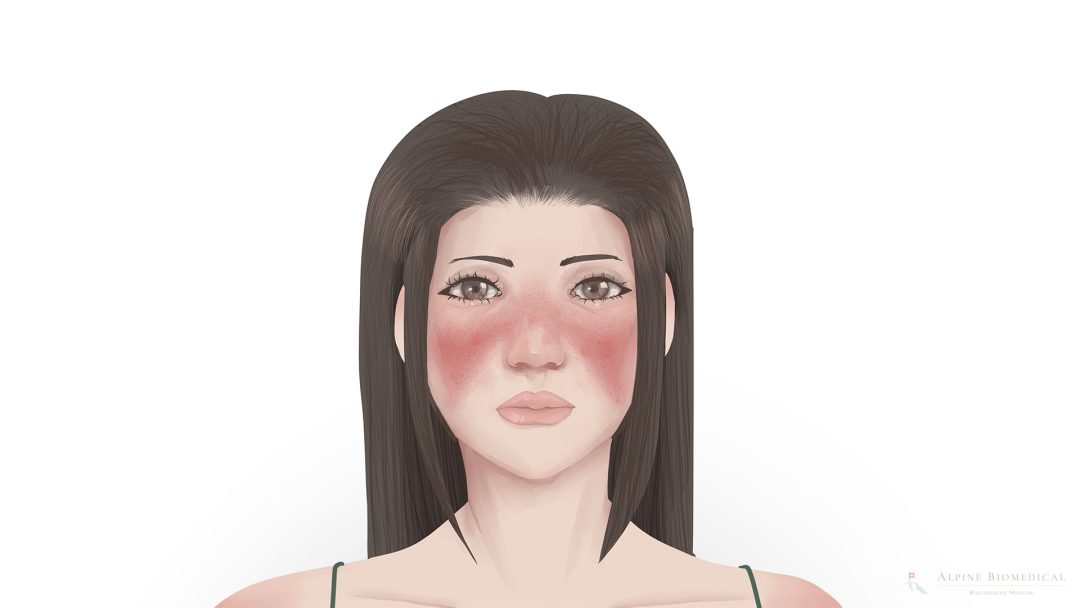
- Butterfly rash on the face
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Dryness of mucous membranes
- Fever
- Joint pain and headaches
- Chest pains
- Raynaud's syndrome (white or bluish fingers or toes in cold conditions)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Lupus
The diagnosis of Lupus is based on medical history, physical examinations, blood tests, and, if necessary, imaging procedures. Early detection is crucial for better control of flare-ups and minimizing organ damage.
Conventional treatment aims to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation to improve the quality of life. Regarding Lupus erythematosus, holistic medical approaches can play a significant role. This includes detoxification measures, especially the elimination of heavy metals and environmental toxins. Harmful immune complexes and toxins can be effectively removed through INUSpheresis therapy, optimizing the effectiveness of further therapeutic measures.
Promoting a healthy gut flora through intestinal cleansing and addressing hidden inflammations in the body also plays a key role.
Dr. med. Karsten Ostermann M.A.
In the treatment of Lupus, addressing the underlying causes is essential. An interdisciplinary approach involving experienced therapists from various fields is advisable.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.