Crohn's Disease
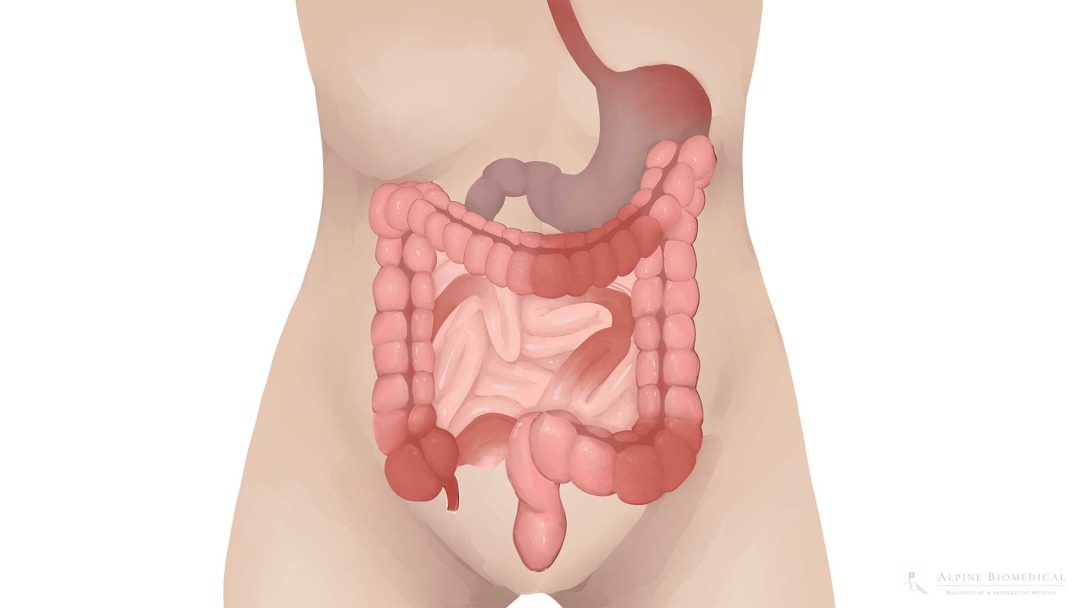
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the entire digestive tract and is associated with periodic relapses and remissions (temporary relief of symptoms). Crohn’s disease mainly affects the end section of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. This disease causes inflammation in the intestinal wall and is associated with numerous symptoms.
Symptoms of Crohn's Disease
Crohn’s disease is characterized by an overactive immune system that causes inflammation in the intestine. This leads to damage to the intestinal wall and the characteristic symptoms of the disease.
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease include:
- Stomach pain and abdominal cramps, predominantly in the right lower abdomen
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Weight loss
- Tiredness, exhaustion and fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
Due to the large inflamed intestinal surface, the disease has a strong effect on the immune system, which needs a lot of energy to work. The result is a permanent lack of energy in affected patients.
Causes of Crohn's Disease
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is not known. It is assumed that it is a multifactorial process and that the causes can reinforce each other.
The causes discussed include:
- Environmental factors
- Eating habits with hidden food intolerances
- Immune disorders with overactivation of the immune system
- Infections with parasites, fungi, bacteria, viruses (e.g. CMV, EBV)
- Psychological trauma
- Genetic predispositions
Diagnosis and Treatment of Crohn's Disease
The diagnosis of Crohn’s disease requires various diagnostic tests, including blood tests, imaging procedures such as MRI or CT scans and endoscopy with biopsy.
Conventional treatment of Crohn’s disease focuses on controlling inflammation, relieving symptoms and preventing complications. This includes the administration of antiinflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants and biologics and, in severe cases, surgical interventions to remove damaged tissue or treat complications such as bowel obstructions.
From an integrative, holistic perspective, intestinal cleanse is another important aspect that aims to correct the disturbed balance of the intestinal flora. An individual approach guided by experienced therapists is essential here. Gut rehabilitation is increasingly seen as an integral part of holistic medicine and can include various methods such as colon hydrotherapy and infusion therapy.
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing Crohn’s disease. These include a healthy diet, stress management, regular exercise and abstaining from smoking.
Med. pract. Dana Hreus M.A.
The treatment of Crohn's disease should be based on the individual causes of the disease and should involve therapists from different specialties.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.