Mononucleosis
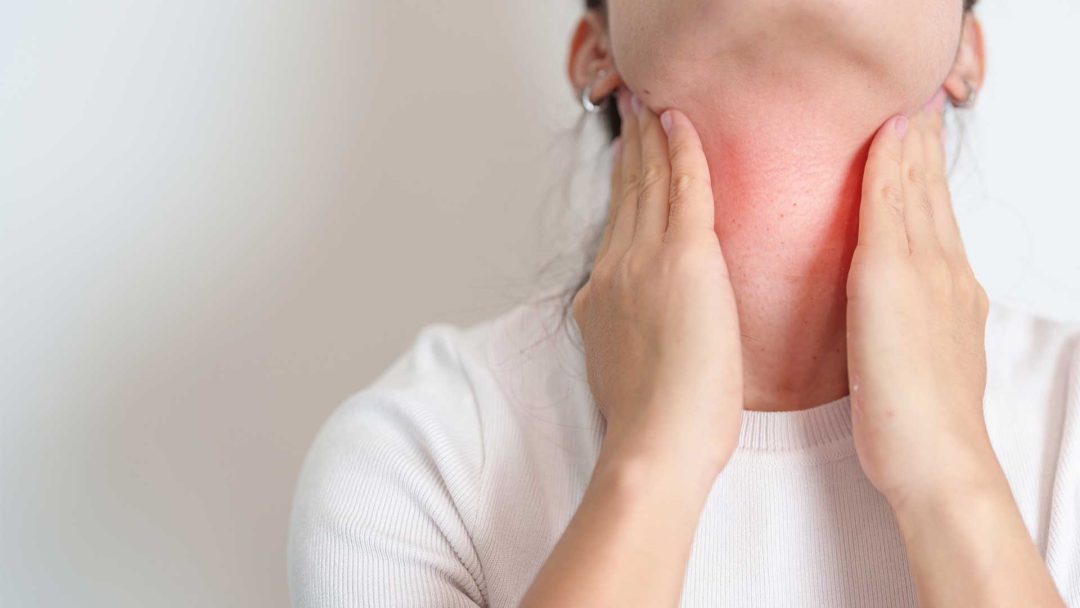
Mononucleosis, also known as Pfeiffer’s glandular fever, mono or kissing disease, is a viral disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Typical symptoms include persistent fatigue, exhaustion, fever, sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes and an enlarged spleen. Sometimes skin rashes or jaundice also occur. The diagnosis is based on the symptoms, physical examination and special blood tests that can detect antibodies against EBV. Customised, integrative treatments such as hyperthermia, ozone therapy or infusion therapy can provide effective support.
Dr. med. Karsten Ostermann M.A.
Mononucleosis can severely weaken the person affected and cause lasting health consequences. A cause-oriented therapy with experts from different disciplines and individually adapted treatment methods can achieve a long-lasting improvement in mononucleosis.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.