Hemorrhoids
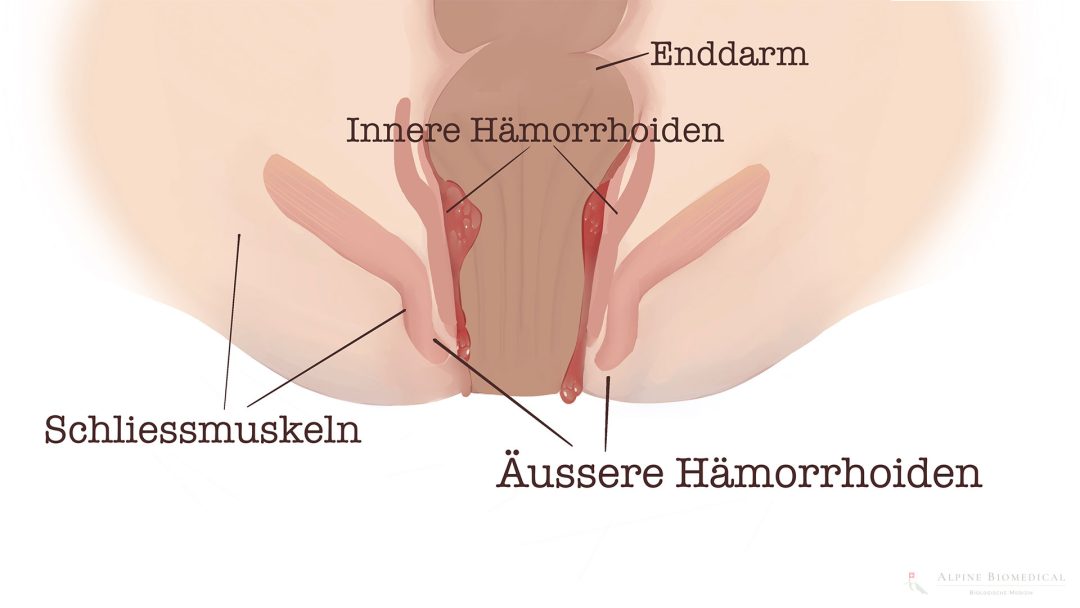
Hemorrhoids are dilated veins in the anal area that can cause discomfort such as itching, pain and bleeding. These conditions are caused by increased pressure in the rectal area due to factors such as chronic constipation, prolonged sitting, pregnancy or a genetic predisposition.
There are varying degrees of hemorrhoids, from mild swelling to severe discomfort and prolapse. Treatment often involves a combination of lifestyle changes such as a high-fiber diet to regulate stool, adequate fluid intake and regular exercise.
Hemorrhoid Causes
There are several causes of hemorrhoids, and these can often work together to exacerbate symptoms.
The causes include:
Impaired Intestinal Health
A disorder in the bowel can lead to constipation or diarrhea. Both can promote the development of hemorrhoids. Intestinal health plays a very important role in the development of hemorrhoids.
Unhealthy Diet
An unhealthy diet can severely affect intestinal health. Constipation is often the result, which can lead to hemorrhoids.
Lack of Exercise
A lack of exercise can make bowel activity sluggish and also lead to constipation.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy increases the pressure on the internal organs and the connective tissue becomes looser and more elastic in preparation for the birth. Pregnancy favors the development of haemorrhoids.
Lifting heavy Loads
When lifting heavy loads, the pressure on the bowel is greatly increased for a short time. If the veins in the anal area are already weak, hemorrhoids can develop.
Weak connective Tissue
Congenital or acquired connective tissue weakness can also promote hemorrhoids. Acquired connective tissue weakness can occur in connection with various diseases or due to micronutrient deficiencies.
Haemorrhoid Symptoms
Initially, hemorrhoids can develop unnoticed or cause only a few symptoms. As the hemorrhoids increase in size, the symptoms usually become more severe.
The symptoms include:
- Blood on the toilet paper and in the stool
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation
- Itching, burning
- Oozing
- Pain and inflammation
The feeling of incomplete evacuation can cause sufferers to go to the toilet more frequently and further exacerbate the symptoms.
It is crucial to seek medical advice at an early stage, as untreated hemorrhoids can lead to further complications.
Hemorrhoid Diagnosis
Hemorrhoids can be diagnosed by clinical examination.
A thorough intestinal diagnosis of the entire intestine is recommended, as the intestine should be considered as a whole in order to identify profound causes such as digestive disorders, enzyme deficiency, intestinal dysbiosis, intestinal overgrowth (SIBO) and leaky gut (intestinal permeability).
Micronutrients should also be examined in order to identify possible deficiencies and compensate for them individually.
Treating Hemorrhoids
The classic treatments use ointments that are applied locally to the hemorrhoids. In some cases, minimally invasive procedures or surgical interventions are also recommended.
Natural measures include, for example, warm sitz baths with the addition of arnica, camomile, bloodroot or oak bark.
In order to treat the causes, an individually adapted intestinal cleanse should be carried out. It is also important to correct possible micronutrient deficiencies through orthomolecular therapy or with the help of infusions.
Med. pract. Dana Hreus M.A.
If left untreated, hemorrhoids can lead to further health problems. It is important to consult an experienced doctor in good time.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.