Gout
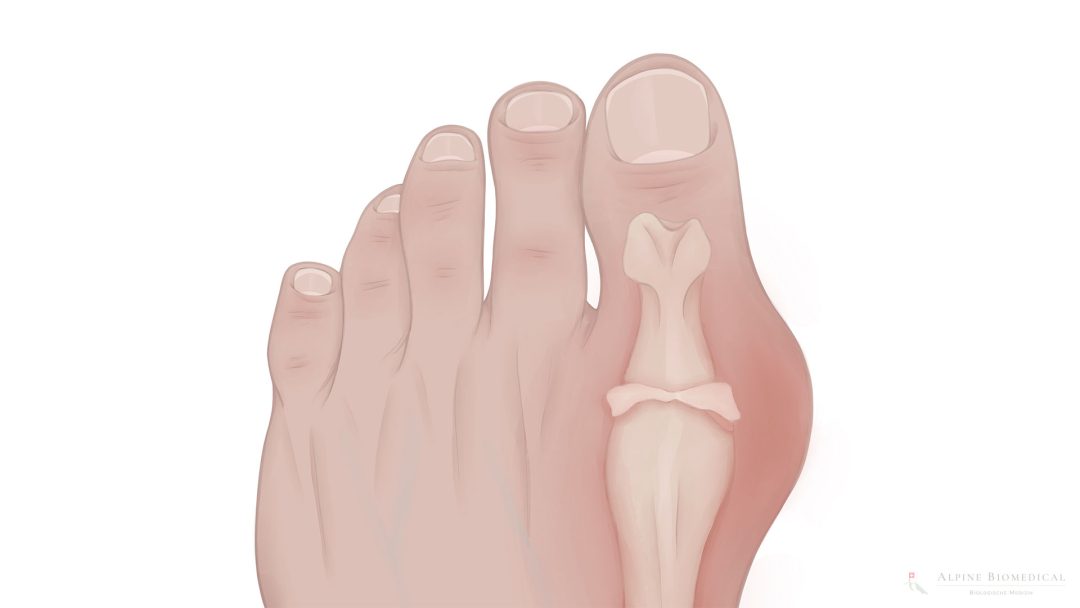
Gout is an inflammatory and painful joint disease characterized by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia). The high level of uric acid leads to the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints, which causes the typical inflammation and pain.
Gout also increases the risk of arthritis, kidney disease and high blood pressure.
Gout Symptoms
Gout is an inflammatory disease that mainly affects the joints. It causes symptoms such as
- Pain on touch and movement
- Redness and overheating
- Swelling
- Restriction of the function of the affected joint
- Occasionally fever and general symptoms of illness
Causes of Gout
Gout is caused by an excessive build-up of uric acid in the body. Reasons for this can be:
- Reduced ability to break down uric acid enzymatically
- Reduced ability to excrete uric acid (especially via the urine)
- Increased consumption of foods rich in purines (nitrogenous compounds), for example meat, certain types of fish, crustaceans and beer
- Excessive production of purines in the liver
Other causes are:
- Genetic predispositions
- Stress
- Excessive consumption of alcohol
- High consumption of fructose in drinks and food
- Dysbiosis in the gut
- Micronutrient deficiencies
- Anemia, in which there is an excessive breakdown of red blood cells.
- Toxic exposure to lead
- Some medications
- Genetic predisposition
Gout Treatment
The causes of gout should be thoroughly clarified before effective and targeted treatment can be started. On this basis, symptomatic and cause-oriented therapeutic measures can then be selected and continuously adapted.
Symptomatic measures focus on relieving acute pain attacks with anti-inflammatory medication and cooling measures.
Holistic, cause-oriented medical treatment can include the following therapeutic approaches:
- Detoxification measures, to eliminate toxic metals
- Intestinal cleansing, to promote healthy intestinal flora.
- Change of diet to a plant-based diet
- Supply of missing micronutrients
- Infusion therapy
- Laser therapy
- Ozone therapy
- Leech therapy
- Sanum therapy
Gout Diet
People with gout should adjust their diet in consultation with an experienced doctor. When adapting your diet, you should avoid getting into an imbalance and developing deficiencies.
In general, foods with a high purine content, such as various types of meat, fish, seafood and beer, should be avoided. It is also important to reduce the consumption of foods with a high fructose content.
Gout Flares
A gout flare-up, also known as a gout attack, is an acute worsening of the condition. The signs of inflammation and pain come to a head and can be very distressing for those affected. In such cases, action should be taken quickly to alleviate the symptoms and prevent damage to the organs. Anti-inflammatory measures, both medicinal and naturopathic, can be used effectively and intercept the gout flare-up.
Pseudogout
Pseudogout is also known as chondrocalcinosis and leads to symptoms that are similar to classic gout. It is a metabolic disease in which calcium pyrophosphate crystals (not uric acid crystals) are deposited in the joints. An experienced doctor can recognize these on ultrasound and differentiate pseudogout from gout.
Dr. med. Karsten Ostermann M.A.
Patients with suspected gout should definitely undergo a full, cause-oriented diagnosis. The therapy can be better planned and managed based on the results.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.