Thyroid Diseases
Thyroid diseases are various disorders that can affect the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a small gland in the neck that produces hormones that control metabolism and many other vital functions in the body. Thyroid disorders are common in modern times and can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the type of disorder.
Below are some common thyroid disorders:
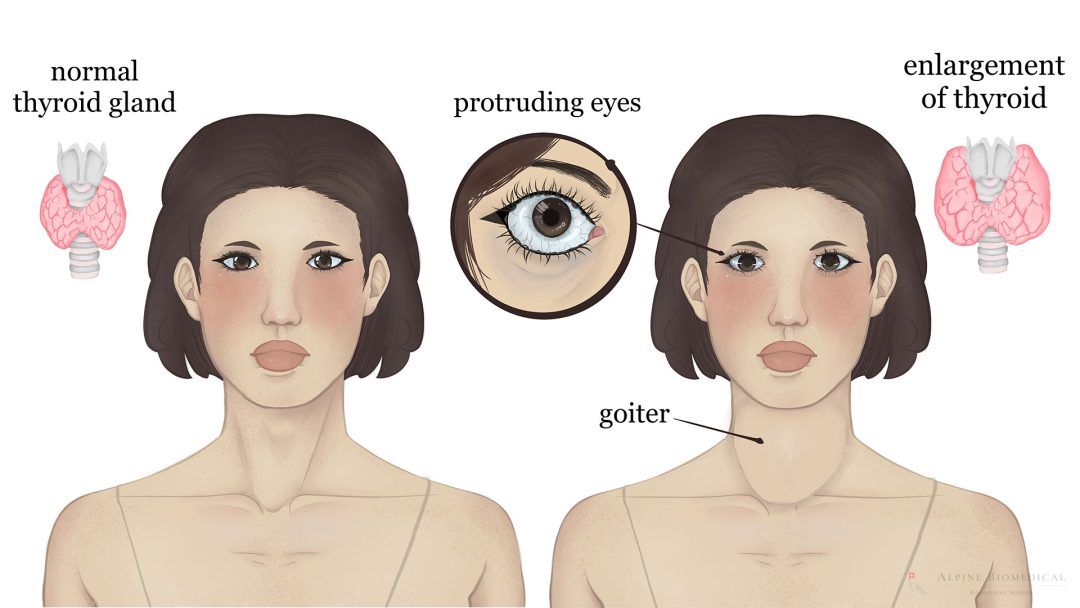
Graves’ Disease
Graves' Disease is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system produces antibodies that are directed against the thyroid gland.
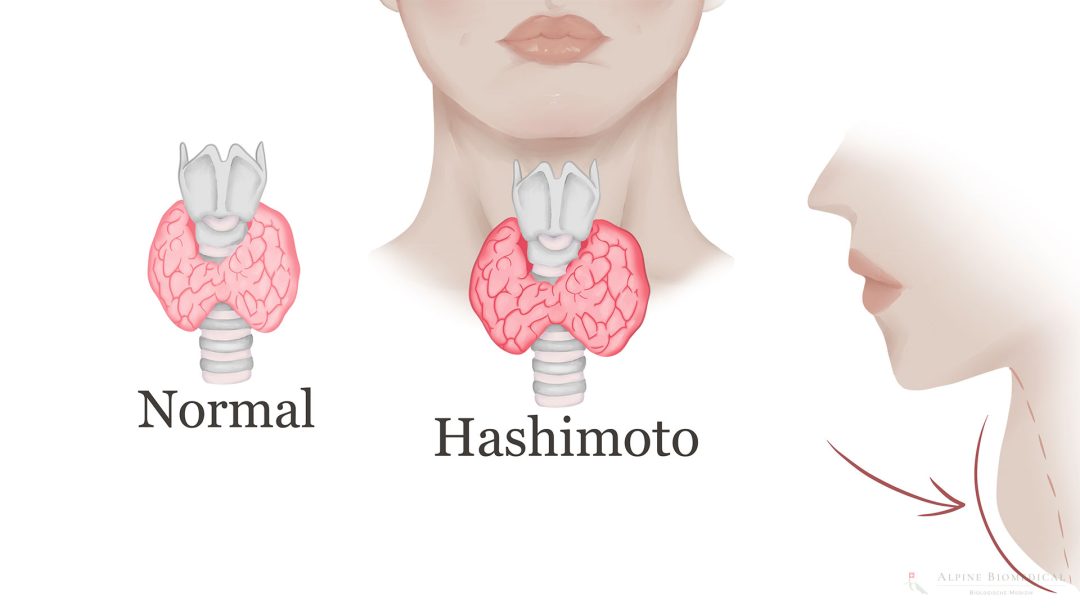
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease of the thyroid gland.

Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is characterised by reduced production of thyroid hormones.

Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition of an excessive production of thyroid hormones.

Types of Thyroid Disease
A common thyroid disorder is hypothyroidism, also known as underactive thyroid. In this condition, the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, which can lead to symptoms such as tiredness, fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, constipation and depression. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disease called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
On the other hand, there is hyperthyroidism. In this case, the thyroid gland produces too many hormones, which can lead to symptoms such as weight loss, nervousness, palpitations, sweating and sleep problems. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is the autoimmune disease Graves’ disease.
In addition to these two main diseases, thyroid nodules can also occur, which can be either benign or malignant. Thyroid nodules can be caused by various factors, including iodine deficiency, inflammation or genetic predispositions.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Thyroid Disorders
The diagnosis of thyroid disorders usually involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests to measure thyroid hormones, imaging such as ultrasound and, if necessary, a fine needle biopsy to examine thyroid nodules.
The treatment of thyroid disorders depends on the specific diagnosis. Treatment for hypothyroidism may involve the substitution of L-thyroxine to balance hormone levels in the body. For hyperthyroidism, various approaches can be used, including medication to block hormone production, radioiodine therapy or, in some cases, surgery to remove the thyroid gland or part of it.
From a holistic medicine perspective, gut health, toxic stress, but also deficiencies of important micronutrients should be considered.
Overall, appropriate diagnosis and treatment of thyroid disorders is important as they can have a variety of effects on health and well-being.
Close collaboration with endocrinologists is often crucial to ensure the best possible treatment.
All Blog Categories
See all blog categories below.
- Allergies
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Bone and Joint Diseases
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Chronic Pain
- Dementia
- Detoxification
- Ear Diseases
- Exhaustion
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Immune Disorders
- Infectious Diseases
- Inflammation
- Intolerances
- Medication
- Men's Health
- Menopause
- Metabolic Disorders
- Minerals
- Neurological Diseases
- Nutritional Supplements
- Respiratory Diseases
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Diseases
- Thyroid Diseases
- Trace Elements
- Tumor
- Vitamins
- Women's Health