Herniated Disc
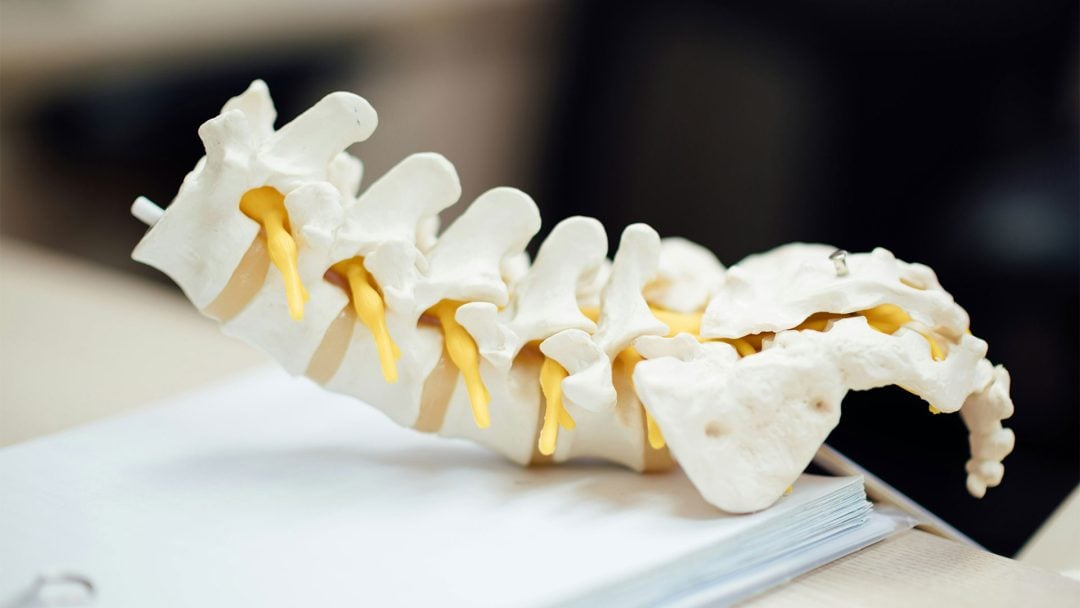
A herniated disc (prolapse) results from a tear in the fibrous outer ring of the intervertebral disc (annulus fibrosus), causing parts of the gel-like inner core (nucleus pulposus) to protrude into the spinal canal and compress the nerves. Affected individuals suffer from severe, radiating back pain.
Causes of Herniated Discs
The causes of herniated discs often involve degenerative processes within the disc itself, leading to a gradual loss of structural stability and protrusion of the inner core into the spinal canal. This degenerative process is exacerbated by an unhealthy diet and lack of exercise, excessive strain due to postural errors or previous injuries. Certain sports that compress, jar, or twist the spine, such as horseback riding, skiing, squash, tennis, or golf, also contribute to the causes and should not be excessively practiced by predisposed individuals.
Structural changes in the jaw joints, caused by functional bite problems, can affect the entire structural system of the body and ultimately predispose to herniated discs. Such a condition is referred to as TMJ and is very common.
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the affected area of the spine. They may include localized back pain radiating into the arms or legs, restricted movement, and numbness in the corresponding segment.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Herniated Discs
Diagnosis of a herniated disc involves neurological examination and imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans.
Treatment depends on the severity and ranges from conservative approaches such as rest, pain medication, and physiotherapy to interventional pain therapy with injections. The primary treatment approach is to work on reducing inflammation to alleviate irritation of the nerve root. This could involve hyperthermia, anti-inflammatory infusions, taking anti-inflammatory supplements, and periradicular therapy with autologous therapeutics.
In cases of progressive symptoms or emerging neurological deficits, surgical intervention is fortunately relatively rare.
Prevention of Herniated Discs
It is crucial to take preventive measures to prevent herniated discs. These include regular exercise, balanced nutrition, correct posture, and avoiding heavy lifting. Additionally, there are various complementary medicine preventive approaches.
Med. pract. Dana Hreus M.A.
For herniated discs, an individualized concept that aims not only to alleviate symptoms but also to treat the underlying causes of the problems is highly recommended.

Further information
The information listed contains relevant topics and serves to improve understanding.